The International Baccalaureate®

The International Baccalaureate aims to nurture young individuals who care about others and the world and strive to promote a better, more peaceful planet through intercultural understanding and respect. IB programs encourage students worldwide to be active, empathetic, and lifelong learners, recognizing that people’s differences can lead to diverse perspectives, all of which can also be right. IB students take responsibility for their own learning and understand how knowledge itself is constructed.
Help Students:
Deepen your understanding of the IB philosophy by exploring it further.
IB Learner Profile
IB graduates are distinguished by practice-oriented attributes known as the IB Learner Profile. Each of the IB programs is committed to the development of students according to the IB learner profile. The IB learner profile places the student at the centre of an IB education.
IB learners strive to be: Inquirers, Knowledgeable, Thinkers, Communicators, Principled, Open-minded, Caring, Risk-takers, Balanced, and Reflective.

© International Baccalaureate Organization 2024
To learn more about the IB Learner Profile, please visit the following link
The Interplay of Inquiry, Action, and Reflection
The goal of IB programmes is to foster a diverse set of skills and attitudes that empower students to take charge of their learning and effectively assess their progress. This approach is symbolized by the interplay between inquiry (asking), action (doing), and reflection (thinking). IB education promotes open classrooms that value and appreciate various viewpoints and perspectives.
1. Inquiry: Sustained inquiry is at the core of IB curricula, framing what is taught, assessed, and learned.
2. Action: Principled action is both a strategy and an outcome, embodying the IB’s commitment to teaching and learning through practical, real-world experience.
3. Reflection: Critical reflection is the process by which curiosity and experience can lead to deeper understanding. Learners must become critically aware of the way they use evidence, methods, and conclusions.
Approaches to Learning (ATL)
The IB emphasizes “learning how to learn” and identifies five categories of interrelated skills called Approaches to Learning (ATL) to empower students to become self-regulated learners, ask good questions, set effective goals, pursue their aspirations, and have the determination to achieve them.
Five ATL skills include:
1. Thinking Skills: Critical thinking, creative thinking, and ethical thinking.
2. Research Skills: Comparing, contrasting, validating, and prioritizing information.
3. Communication Skills: Written and oral communication, effective listening, and formulating arguments.
4. Social Skills: Forming positive relationships, active listening, and conflict resolution.
5. Self-Management Skills: Organizational skills like time management and affective skills such as managing motivation and mindset.
Approaches to Teaching
IB programmes employ six key approaches to teaching that are consistent across all programs:
1. Inquiry-Based: Encouraging students to seek information independently and construct their own understanding.
2. Concept-Driven: Exploring concepts to deepen disciplinary knowledge and facilitate connections across different contexts.
3. Contextualized: Using real-life examples and local/global contexts to relate new information to student’s experiences and the world around them.
4. Collaborative: Promoting effective teamwork and fostering a collaborative relationship between teachers and students.
5. Inclusive and Differentiated: Removing barriers to learning, embracing diversity, and creating opportunities for each student to pursue personal goals.
6. Informed by Assessment: Recognizing the vital role of assessment in supporting and measuring learning while providing effective feedback.
The International Baccalaureate® programs share a common focus on international mindedness and developing the attributes of the IB Learner Profile. Despite this shared foundation, each program has its distinct identity and appropriate elements based on students’ developmental stages. IB programs provide students with a curriculum that is broad and balanced, conceptual and interconnected.
As an authorized school of The International Baccalaureate®, Newton Free School offers students access to globally recognized study programs:
1. The Primary Years Programme is for students aged 5-12 years (Grades 0-5)
2. The Middle Years Programme is for students aged 11-16 years (Grades 6-10)
3. The Diploma Programme is for students aged 16-19 years (Grades 11-12)
In the Primary Years Programme (PYP), students explore six transdisciplinary themes of global significance, including topics like our identity (who we are), historical context (where we are in place and time), self-expression (how we express ourselves), how the world functions (how the world works), social organization (how we organize ourselves), and our responsibility to the planet (sharing the planet). To learn more about the programme, please visit the following links: Preschool PYP, Primary Years Programme
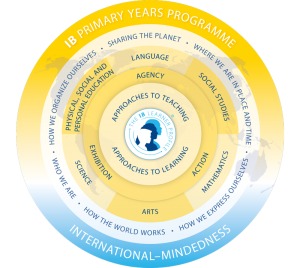
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2024
In the Middle Years Programme (MYP), students explore six interdisciplinary global contexts. These contexts cover areas such as identities and relationships, personal and cultural expression, orientation in space and time, scientific and technical innovation, fairness and development, and globalization and sustainability. To learn more about the programme, please visit the following link: Middle Years Programme
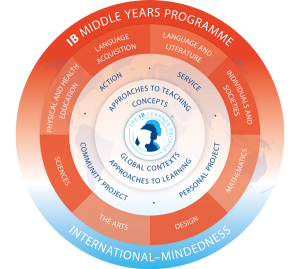
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2024
The Diploma Programme (DP) consists of six disciplinary subject groups and three elements of the DP core: Theory of Knowledge (TOK), the Extended Essay (EE), and Creativity, Activity, Service (CAS). Among these core elements, the theory of knowledge (TOK) course encourages students to reflect on their own perspectives and assumptions by investigating the fundamental question of “how we know what we know”. To learn more about the programme, please visit the following link: Diploma Programme
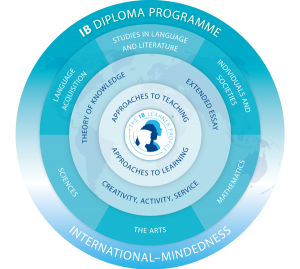
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2024
The IB Diploma has a special status at 1931 universities worldwide. IB students apply to more than 3,300 higher education institutions each year, in close to 90 countries.
Top Universities Attended by IB Graduates:
- Harvard University
- Stanford University
- Yale University
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
- University of Oxford
- University of Cambridge
- Princeton University
- California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
- University of Chicago
- Imperial College London
Newton Free School’s 2023 DP cohort of 20 students received a $2,700,000 scholarship and 80 letters of acceptance from the leading universities in the United States of America, Canada, Great Britain, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, Italy, Belgium, Austria, the Czech Republic, France, and Hungary.
IB Students
1. University Acceptance Rates: IB students generally have higher acceptance rates into prestigious universities compared to students from other programs. Many universities value the rigorous and well-rounded education provided by the IB curriculum.
2. Higher Average Scores: IB students often achieve higher average scores in standardized tests and examinations compared to students in other educational programs.
3. College Readiness: IB students tend to be well-prepared for the challenges of higher education, as the program emphasizes critical thinking, research skills, and independent learning.
4. Performance in Specific Subjects: Studies have shown that IB students tend to perform well in areas such as mathematics, sciences, and languages.
International Baccalaureate® statistics demonstrate the global reach and academic excellence associated with the program, as well as the significant advantages it provides to students in their university education and beyond. Review key findings from research on the impact of International Baccalaureate programmes:

